The fibrinogen story – a tale of what happens following kidney injury
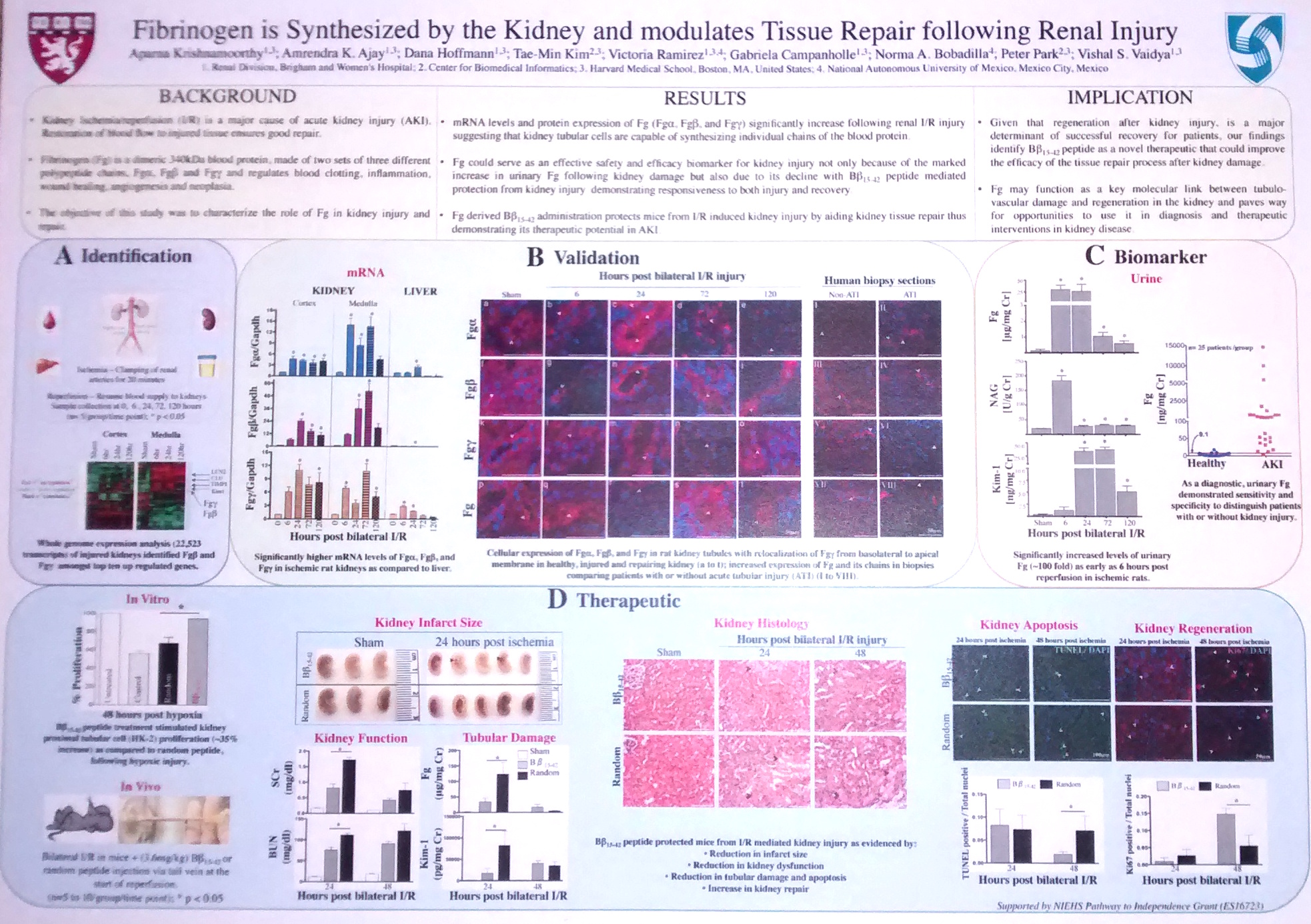
I identified for the first time that fibrinogen, a protein typically expressed in the liver and found in the blood, is in fact expressed and significantly regulated in the kidney after acute kidney injury. I also demonstrated the novel therapeutic potential of a fibrinogen-derived peptide that protects the kidney from kidney injury by increasing kidney tissue repair and decreasing damage to the kidney tissue architecture. The impact of my findings significantly improves the prognosis and treatment options that can be made available to patients with acute kidney injury.
Related publication:
Fibrinogen β–derived Bβ15-42 peptide protects against kidney ischemia/ reperfusion injury
Abstract
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in the kidney is a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) in humans and is associated with significantly high mortality. To identify genes that modulate kidney injury and repair, we conducted genome-wide expression analysis in the rat kidneys after I/R and found that the mRNA levels of fibrinogen (Fg)α, Fgβ, and Fgγ chains significantly increase in the kidney and remain elevated throughout the regeneration process. Cellular characterization of Fgα and Fgγ chain immunoreactive proteins shows a predominant expression in renal tubular cells and the localization of immunoreactive Fgβ chain protein is primarily in the renal interstitium in healthy and regenerating kidney. We also show that urinary excretion of Fg is massively increased after kidney damage and is capable of distinguishing human patients with acute or chronic kidney injury (n = 25) from healthy volunteers (n = 25) with high sensitivity and specificity (area under the receiver operating characteristic of 0.98). Furthermore, we demonstrate that Fgβ-derived Bβ15-42 peptide administration protects mice from I/R-induced kidney injury by aiding in epithelial cell proliferation and tissue repair. Given that kidney regeneration is a major determinant of outcome for patients with kidney damage, these results provide new opportunities for the use of Fg in diagnosis, prevention, and therapeutic interventions in kidney disease.